Adversarial and Implicit Modality Imputation with Applications to Depression Early Detection
Published in CAAI International Conference on Artificial Intelligence (CICAI), 2022
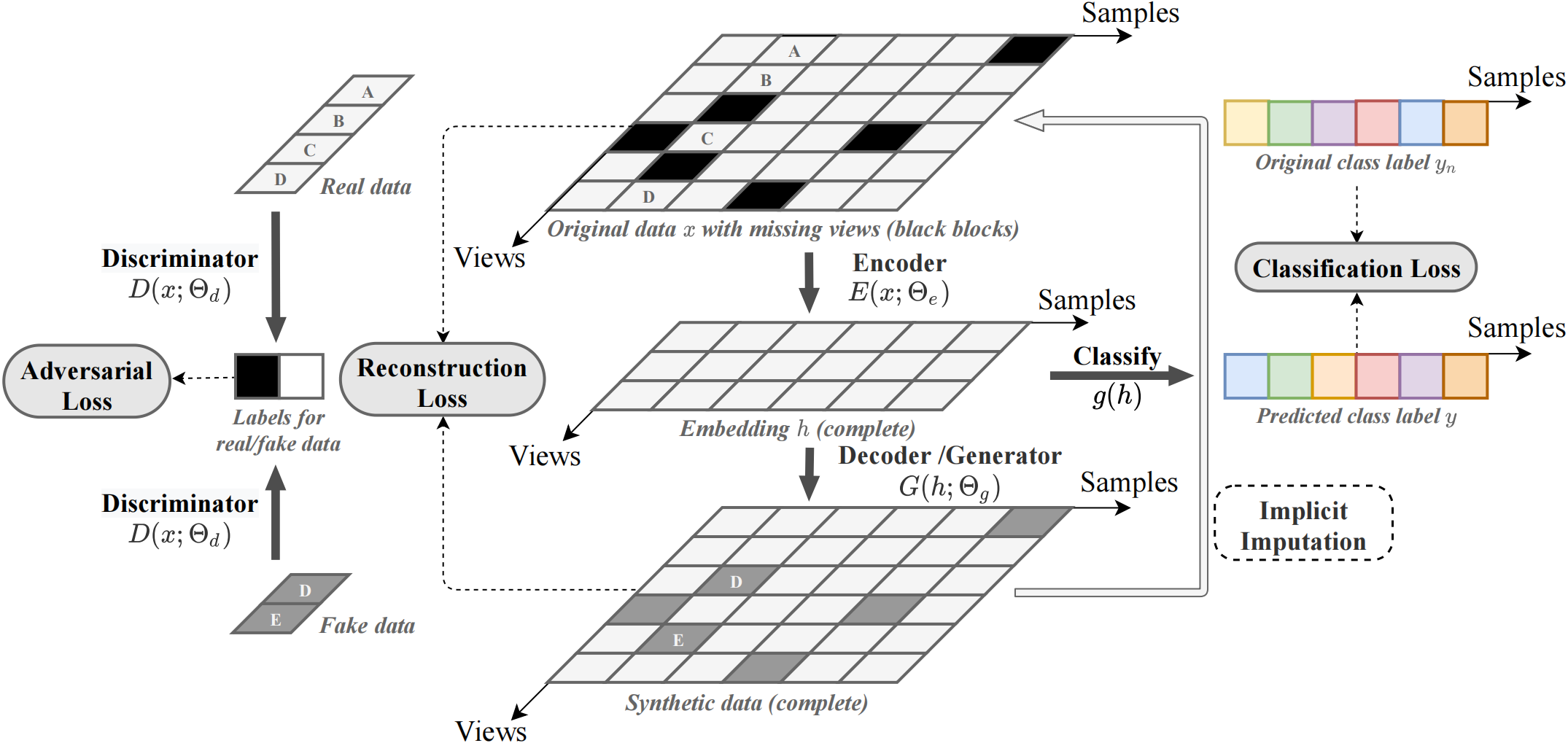
Depression early detection is a significant healthcare task that heavily relies on high-quality multi-modal medical data. In practice, however, learning a robust detection model is challenging because real-world data often suffers from serious modality-level missing issues caused by imperfect data collection and strict data sharing policies. In this study, we propose an Adversarial and Implicit Modality Imputation (AIMI) method to resolve this challenge. In particular, when training multi-modal predictive models, we learn an implicit mechanism to impute the missing modalities of training data at the same time. These two learning objectives are achieved jointly in an adversarial learning framework. Based on the UK Biobank dataset, we demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of our method on the early detection of depression.
